NASA Removes ‘Stubborn’ Fasteners
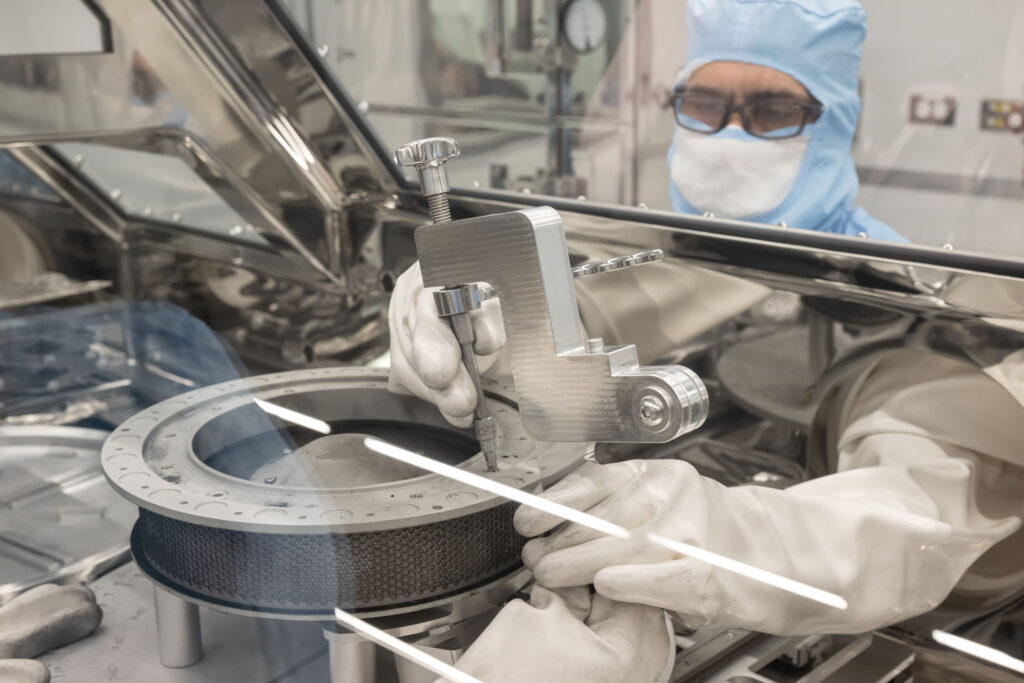


OSIRIS REx curation team attempting to remove two stuck fasteners prohibiting the complete opening of the TAGSAM head.
NASA experts at Johnson Space Center in Houston have successfully removed the final two fasteners from the sampler head that had prevented the remainder of OSIRIS-REx’s asteroid Bennu sample material from being accessed.
“Our engineers and scientists have worked tirelessly behind the scenes for months to not only process the more than 70 grams of material we were able to access previously, but also design, develop, and test new tools that allowed us to move past this hurdle,” said Eileen Stansbery, division chief for ARES (Astromaterials Research and Exploration Science) at Johnson.
Work to retrieve the material stalled in October after two of the 35 fasteners could not be removed with the tools approved for use inside the OSIRIS-REx glovebox.
In response, two new multi-part tools were designed and fabricated to support further disassembly of the TAGSAM head. These tools include newly custom-fabricated bits made from a specific grade of surgical, non-magnetic stainless steel; the hardest metal approved for use in the pristine curation gloveboxes.
“In addition to the design challenge of being limited to curation-approved materials to protect the scientific value of the asteroid sample, these new tools also needed to function within the tightly-confined space of the glovebox, limiting their height, weight, and potential arc movement,” said Dr. Nicole Lunning, OSIRIS-REx curator at Johnson. “The curation team showed impressive resilience and did incredible work to get these stubborn fasteners off the TAGSAM head so we can continue disassembly.”
Prior to the successful removal, the team at Johnson tested the new tools and removal procedures in a rehearsal lab. After each successful test, engineers increased the assembly torque values and repeated the testing procedures until the team was confident the new tools would be able to achieve the torque needed while minimizing the risk of any potential damage to the TAGSAM head or any contamination of the sample within.
Steps now are underway to complete the disassembly of the Touch-and-Go Sample Acquisition Mechanism, or TAGSAM, head to reveal the rest of the rocks and dust delivered by NASA’s first asteroid sample return mission.


There are no comments at the moment, do you want to add one?
Write a comment